Elo Rating Change Calculator
This section will calculate the change in a player's Elo rating after playing a single game against another player. The value K is the maximum change in rating.Everyone wants to become the best chess player, right? But how do we know where we stand? That’s exactly where the chess rating system comes into play. A chess rating system evaluates a player’s performance relative to others. A higher rating signifies greater skill, while a lower rating indicates room for improvement.
While various rating systems have existed, today the most prominent and widely used one is the Elo rating system, officially adopted by the International Chess Federation (FIDE) in 1970.
What is a FIDE Rating?
A FIDE rating, commonly known as an Elo rating, measures a chess player’s skill level based on their performance against other rated players. Simply put, a higher FIDE rating indicates a stronger chess player.
Check out this detailed guide to understand how to obtain your FIDE rating: How to get a FIDE Rating in Chess.
How Does the FIDE Elo Rating System Work?
The Elo rating system was developed by Arpad Elo, a Hungarian-American physics professor and chess enthusiast. Unlike other rating systems that merely reflect past performance, the Elo system predicts the probability of match outcomes based on player ratings.
Here’s how it works:
- If two players have equal ratings, each is predicted to win half of their games.
- If a player has a rating advantage, they’re predicted to perform better proportionally. For instance, a player rated 200 points higher is expected to win approximately 76% of the time.
This dynamic approach allows fluctuations in a player’s performance to be accurately reflected in their rating adjustments.
How is the FIDE Rating Calculated?
The FIDE Elo system assumes player performance follows a normal distribution—a bell-shaped curve—meaning a player’s performance will fluctuate around a stable average over time. Each player’s new rating after a match is calculated using this formula:
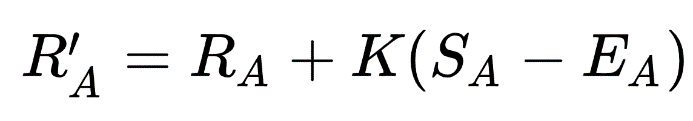
New Rating = Old Rating + K × (Actual Score – Expected Score)
- Expected Score is calculated based on the ratings of both players.
- Actual Score is 1 for a win, 0.5 for a draw, and 0 for a loss.
- K-factor determines how sensitive the rating is to recent results:
- K = 40 for new players (until they have played 30 games or reached a rating of 2300).
- K = 20 for players with a stable rating below 2400.
- K = 10 for players rated 2400 or above.
The larger the K-factor, the greater the impact of recent games on the player’s rating.
Are FIDE Ratings and Elo Ratings the Same?
Yes, the terms FIDE rating and Elo rating generally refer to the same thing. The Elo system is the official rating methodology adopted by FIDE.
Current FIDE Rating Categories
Here’s how players are currently classified based on their FIDE ratings:
| Title | Rating Range |
|---|---|
| Super Grandmaster | 2700 and above |
| Grandmaster (GM) | 2500 – 2699 |
| International Master (IM) | 2400 – 2499 |
| FIDE Master (FM) | 2300 – 2399 |
| Candidate Master (CM) | 2200 – 2299 |
| Class A player | 2000 – 2199 |
| Class B player | 1800 – 1999 |
| Class C player | 1600 – 1799 |
| Class D player | 1400 – 1599 |
Players rated below 1400 typically do not receive published FIDE ratings.
How Can You Get Your First FIDE Rating?
To begin your journey towards becoming a titled player, here’s how you get started:
- Register with your national chess federation to obtain a FIDE ID.
- Participate in official FIDE-rated tournaments.
- Play against a minimum of five FIDE-rated opponents.
- Score at least half a point against these rated opponents within 26 months.
- Achieve an initial rating of at least 1400 to have your rating officially published by FIDE.
Once you meet these criteria, your FIDE rating will be published, and you’ll be officially part of the global chess rating community.
Now, all that’s left is to register, play your best, and start your exciting journey towards chess excellence!
Read More : How to play chess